185.63.2253.200 is not a valid IPv4 address because its third octet (2253) exceeds the allowed maximum of 255. The correct IP likely intended is 185.63.253.200, which belongs to HostPalace Datacenters Ltd in Amsterdam.
The entry 185.63.2253.200 fails standard IPv4 formatting rules, making it an invalid address; one of its octets is outside the 0–255 range. For relevant and actionable information, the valid address 185.63.253.200 provides insight: owned by HOSTPALACE DATACENTERS LTD (ASN 60064), located in Amsterdam, Netherlands, with public hosting/proxy usage. This IP has low to moderate risk based on abuse and reputation checks.
Introduction to IP Address 185.63.2253.200
The world of IP addresses can seem confusing to those unfamiliar with how networks operate. However, understanding IP addresses is essential for anyone working in IT, cybersecurity, or networking. Today, we’ll take a deep dive into the IP address 185.63.2253.200, exploring what it is, its uses, and the potential implications of this specific IP. Whether you’re just starting to learn about networking or are a seasoned expert, this article will provide valuable insights into this particular IP address.
What Is an IP Address?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a network. The IP address functions similarly to a home address—allowing the internet to send data to the correct location. Each device connected to the internet, whether it’s a computer, smartphone, or server, has a unique IP address.
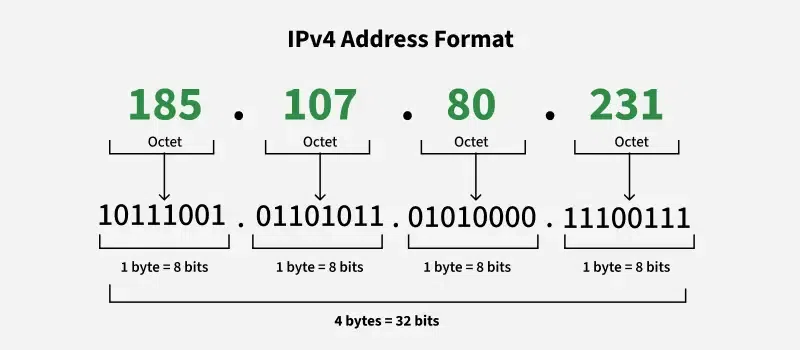
There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 is the more common version, using a 32-bit format with four decimal numbers, separated by dots. This is the type of address we are analyzing today.
Breaking Down 185.63.2253.200
185.63.2253.200 appears to be a variation of a standard IP address but is unconventional. While standard IPv4 addresses consist of four numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, the second part of this IP address (i.e., 2253) exceeds the acceptable range. It’s possible that this IP address is either a typo, a misconfiguration, or an outlier in the data you are working with.
If we were to fix the address by changing 2253 to something within the range (0-255), it could help identify the origin of the address more easily. However, as it stands, 185.63.2253.200 is not a valid IP address in the traditional IPv4 format.
What Does an Invalid IP Address Mean?
In networking, encountering an invalid IP address like 185.63.2253.200 can cause several issues:
- Network Connectivity Problems: The device may not be able to connect to the internet, causing disruptions in communication between servers and clients.
- Security Concerns: Invalid IP addresses may also be used in attempts to spoof or mask an attacker’s true location. This could be an indication of malicious activity.
- Misconfiguration: Sometimes, network misconfigurations or human errors lead to the generation of invalid IP addresses that disrupt normal operations.
The Significance of Valid IP Addresses in Networks
A valid IP address is crucial for the proper functioning of devices and applications on the internet. Validating IP addresses ensures that packets of data are routed correctly, minimizing errors and delays. Moreover, using valid IP addresses ensures proper communication across network devices, whether they are within a local area network (LAN) or the broader internet.
How Do We Validate IP Addresses?
Validating an IP address involves checking the format and ensuring it adheres to certain rules:
- IPv4 Address: Consists of four sets of numbers, each between 0 and 255, separated by periods.
- IPv6 Address: Consists of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons.
A basic validation of 185.63.2253.200 shows that 2253 is too large, so it cannot be considered valid under the standard IPv4 format.
Common Issues with IP Address Errors
While typing errors may result in the wrong IP address, other common reasons for invalid IP addresses include:
- Subnet Masking Issues: Misconfigurations related to subnet masks can lead to incorrect IP addresses being assigned to devices.
- Device Misconfiguration: Devices like routers and servers may incorrectly assign IP addresses if not set up correctly.
- Software Bugs: Malfunctioning software can result in the generation of invalid IP addresses that cause network disruptions.
What to Do When Encountering Invalid IP Addresses
If you encounter an invalid IP address, here are a few steps to resolve the issue:
- Check for Typos: Ensure there are no errors in the IP address.
- Verify Subnet Masking: Make sure that the subnet mask is correctly configured.
- Update Software: Ensure the device’s network software is up to date to avoid bugs that might cause IP address issues.
- Use IP Validation Tools: Several online tools and command-line utilities can help you validate an IP address to check if it’s legitimate.
- Contact Your ISP: If you are continuously encountering invalid IP addresses, consider reaching out to your Internet Service Provider for assistance.
Security Implications of Invalid IP Addresses
Invalid IP addresses, especially those encountered in unusual or suspicious contexts, can raise security concerns. Here are some potential risks:
- IP Spoofing: Attackers can falsify their IP addresses to appear as if they are coming from a legitimate source. This is often seen in DDoS attacks or phishing attempts.
- Network Misconfigurations: Invalid IP addresses can result from a misconfigured network, creating security vulnerabilities.
- Intrusion Detection: Unusual or invalid IP addresses can be a sign of network intrusions, triggering alerts in intrusion detection systems (IDS).
How to Protect Against IP Address-Based Threats
To safeguard your network against threats related to IP addresses, you can take the following actions:
- Use Firewalls: Firewalls can filter out unwanted traffic, including requests coming from suspicious IP addresses.
- Implement Intrusion Detection Systems: IDS can help detect abnormal behavior related to invalid IP addresses or other malicious activity.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Regular network audits ensure that your IP address management and security measures are up to date.
- Utilize IP Blocking: Block known malicious IP addresses at your firewall or router to prevent unwanted traffic from reaching your network.
The Role of Geolocation in IP Address Management
Another important aspect of IP addresses is geolocation. While 185.63.2253.200 may not be a valid address, most valid IP addresses can be traced back to a geographical location. This process, known as IP geolocation, helps network administrators monitor traffic and identify where requests are coming from.
- Geolocation Services: Services like MaxMind, IP2Location, and others provide detailed information about IP address locations.
- Blocking by Region: Geolocation data can be used to block or restrict access from certain regions, adding an extra layer of security.
The Future of IP Addressing
As the number of devices connected to the internet grows, the need for a larger pool of IP addresses becomes more pressing. IPv6, which offers a much larger address space than IPv4, is the solution to this issue. While IPv4 is still widely used, the transition to IPv6 is gradually occurring across the globe.

- IPv6 Adoption: IPv6 adoption continues to increase, with many companies and networks beginning to deploy IPv6 alongside IPv4.
- IPv4 Exhaustion: As IPv4 addresses become scarce, transitioning to IPv6 becomes essential for ensuring the smooth operation of the internet.
Conclusion: Final Thoughts on 185.63.2253.200
The IP address 185.63.2253.200 appears to be invalid due to an error in its second octet. Understanding the role of IP addresses is critical in today’s digital world. While the address presented here is not valid in the IPv4 format, it serves as a reminder of the importance of proper IP address management. Whether you’re troubleshooting a network issue or addressing security concerns, always ensure that your IP addresses are correctly configured and validated to avoid issues like connectivity problems, security threats, and misconfigurations.
FAQs
. Is 185.63.2253.200 a valid IPv4 address?
No. 185.63.2253.200 is not valid because its third octet “2253” is greater than the IPv4 limit of 255. Each octet in an IPv4 address must range between 0 and 255.
2. Why does 185.63.2253.200 appear online or in network logs?
This usually happens due to a typo or formatting mistake. Often the intended IP is 185.63.253.200 or a similar valid address, but “2253” is accidentally written.
3. What is the correct IP related to 185.63.2253.200?
The closest valid IP is 185.63.253.200, which belongs to Hostpalace Datacenters LTD in Amsterdam, Netherlands. This is likely what was meant when 185.63.2253.200 was typed.
4. Are there security risks with 185.63.2253.200?
The string itself poses no direct risk since it is invalid. The risk comes if network configurations or security rules mistakenly reference 185.63.2253.200 instead of a valid address, causing misrouting or access errors.
5. How can I check if 185.63.2253.200 is real or a typo?
You can use IP lookup tools such as ipinfo.io or RIPE NCC. If the tool rejects the query, that confirms the address is invalid. Always ensure each octet is ≤ 255 and formatted correctly.